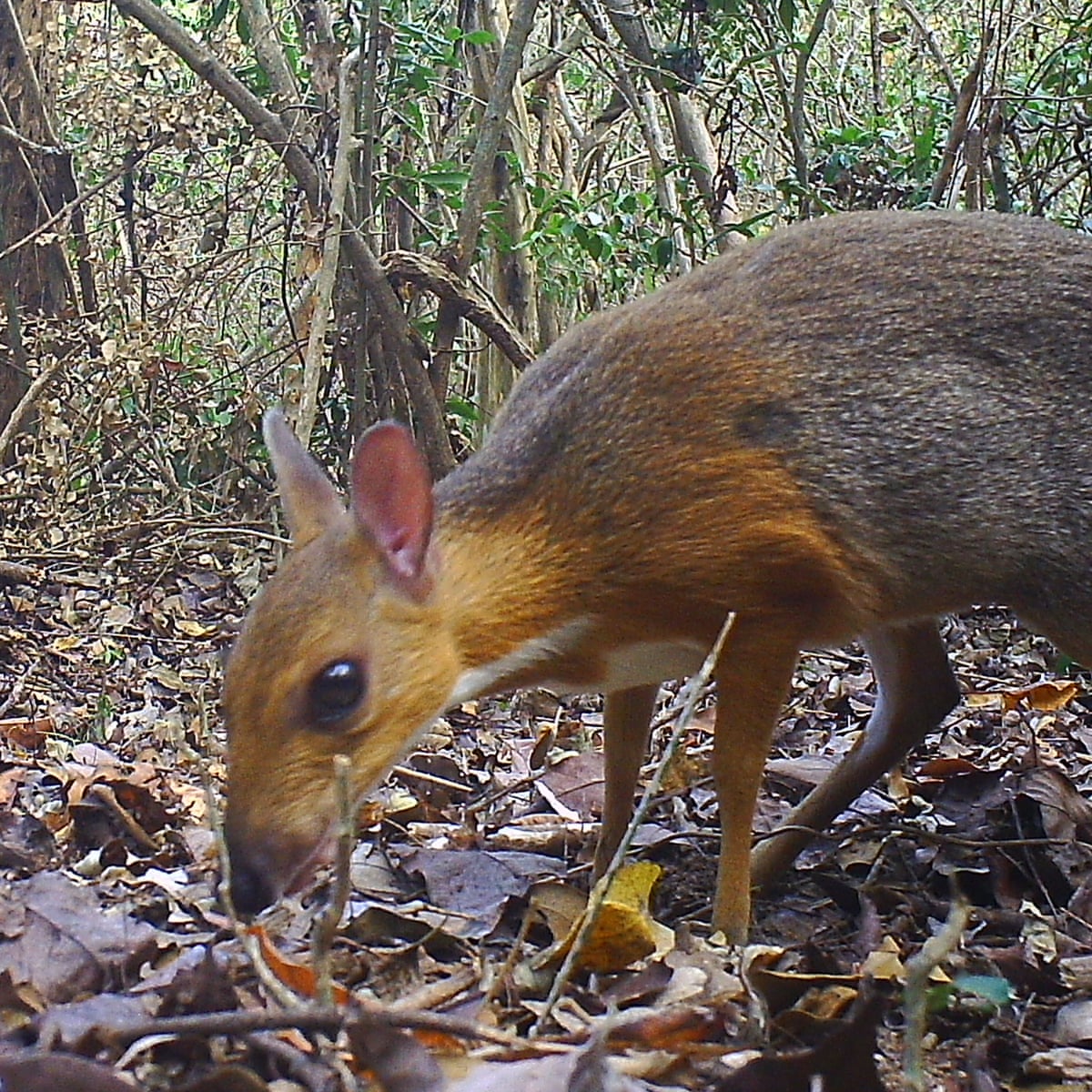
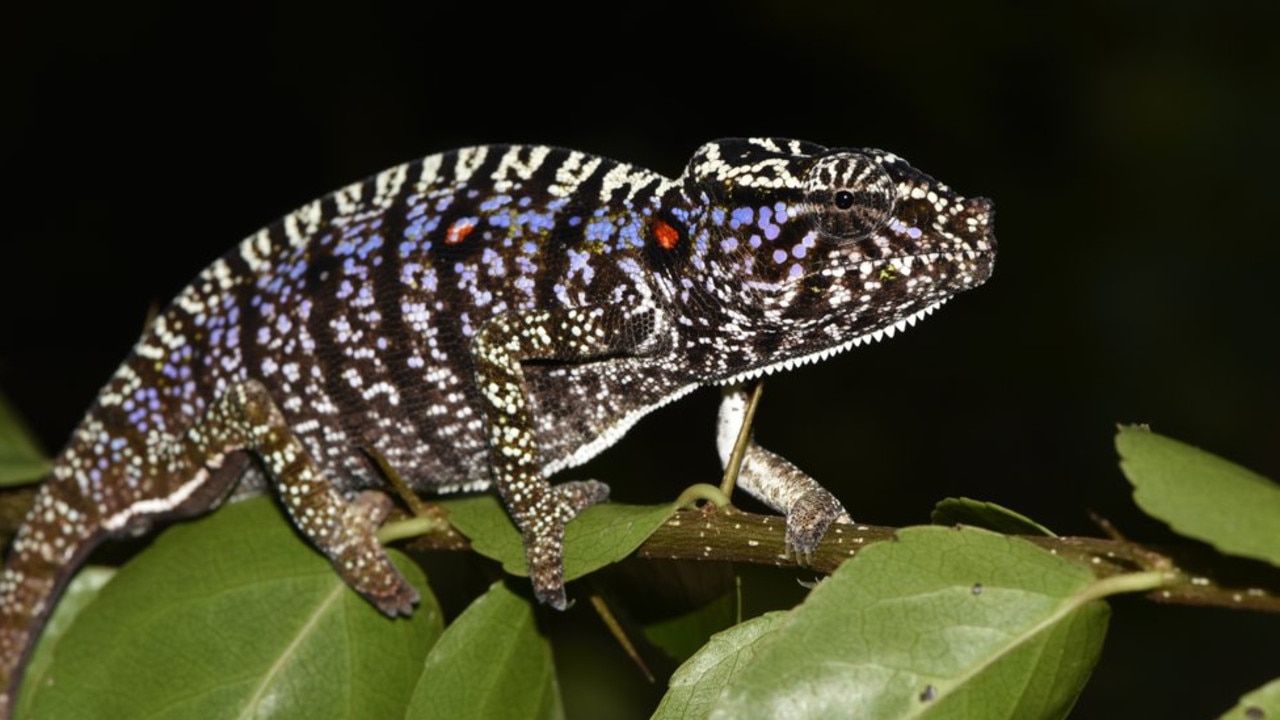
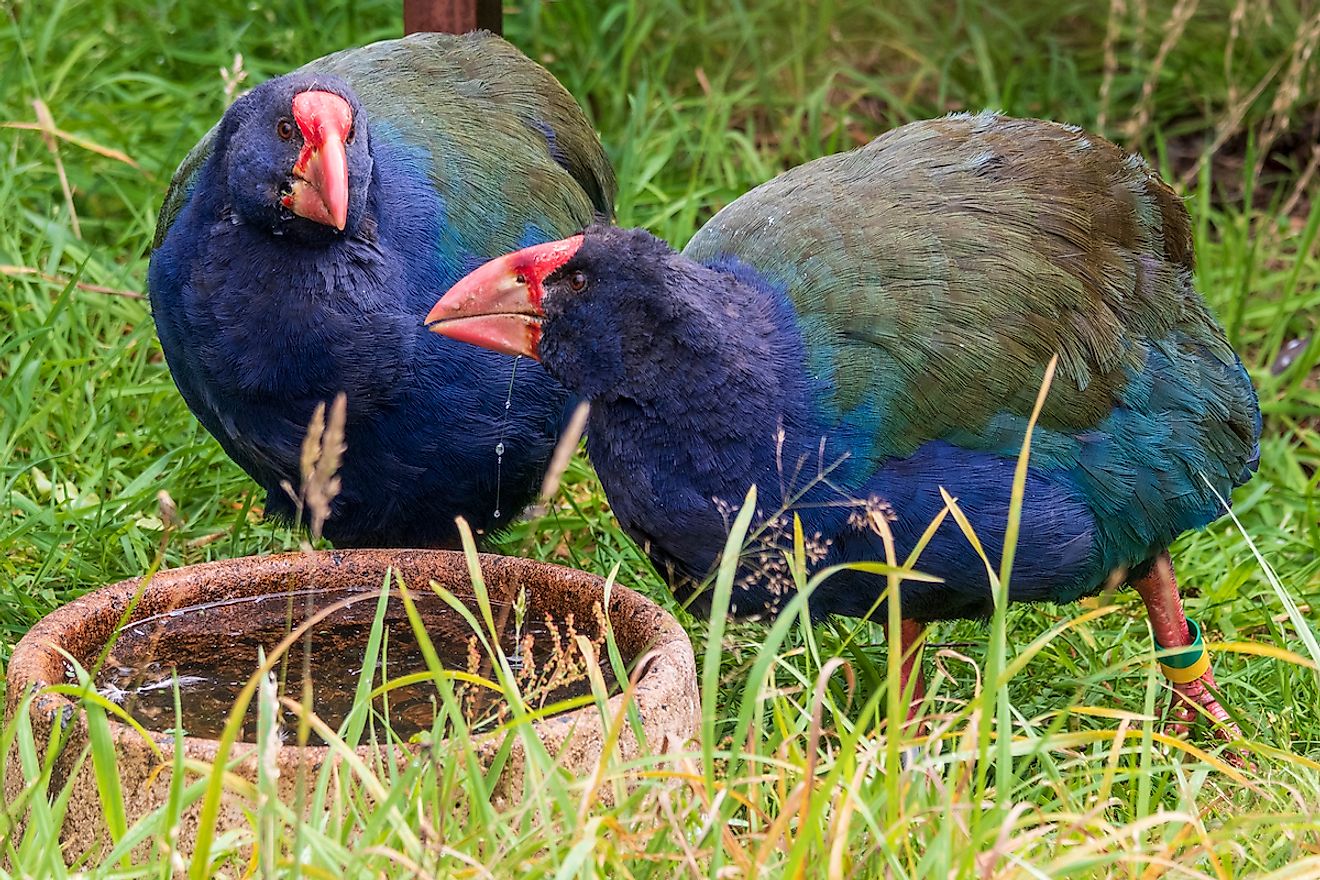
Extinct Animals Found Alive 2017

The baiji were declared extinct in 2006.
Extinct animals found alive 2017. The crested gecko went AWOL for many decades and was believed to be extinct until it was found in. About 15 of the dogs were found in 2017 in the remote Sudirman Mountains in Indonesia which researchers said was enough to make up one thriving pack. Not only has it been 31 years since its been seen but the fish it usually lives within are listed as threatened or endangered from overfishing.
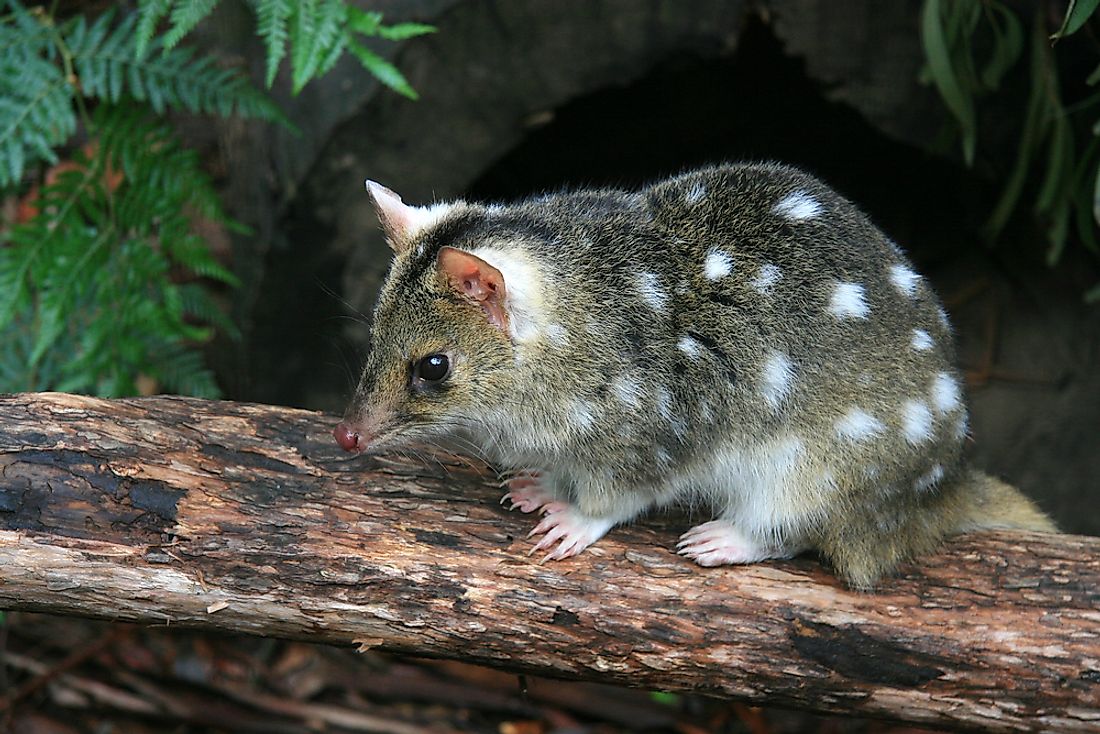
10 Believed Extinct Species Still Alive. It is one of the extinct animals. The medium-sized monitor lizard was since thought lost to science until 2017.
Nonetheless researchers say recent studies show that Pygmy Right Whale qualifies as a living fossil because most of its family lineage went extinct millions of years ago. Its official rediscovery came in early 2019 after a five-day expedition during which a single female was found in a termite nest where the species typically burrows and nests 8 feet off the ground. Tasmanian Tiger May Still Exist.
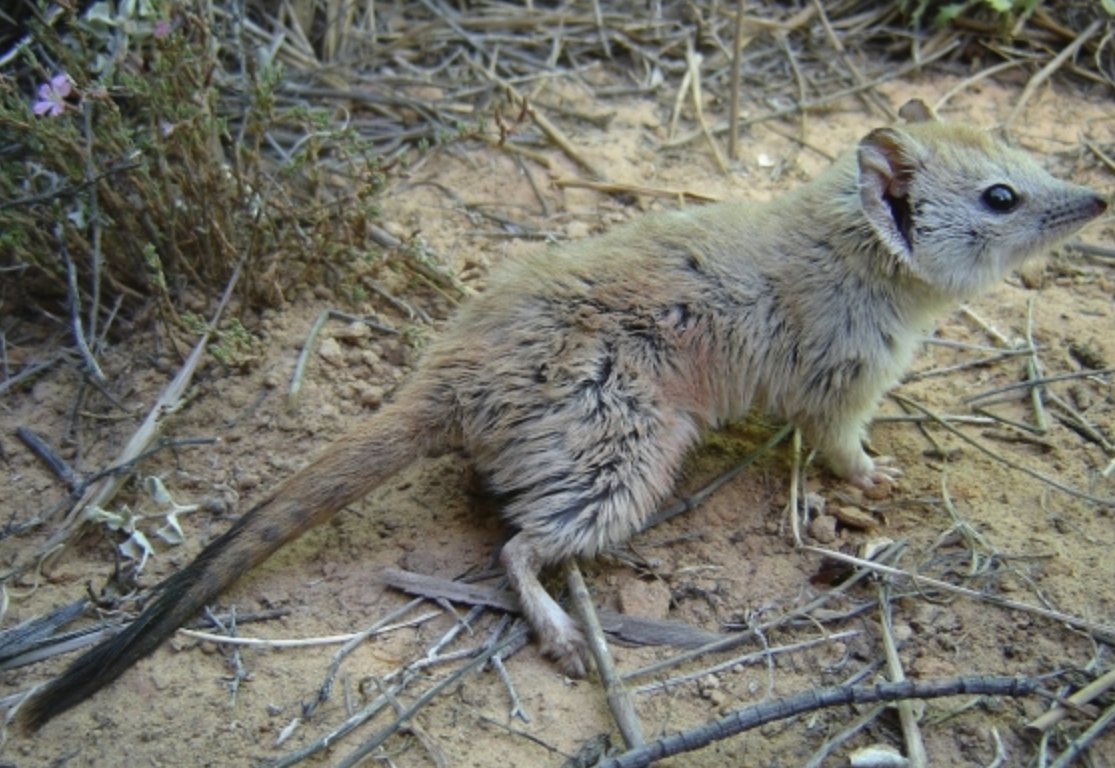
The speedy mouse-sized beast can run at speeds of up to 30kmh and was caught in the very first of 1259 traps set in 12 locations by researchers searching for the missing sengi. The last known member of this species was captured in 1933 and eventually died in a zoo. However this whale species is quite alive and not at all extinct.
These animals once believed to be extinct. Here Are Some Supposedly Extinct Animals Found Alive. Since then the all-star species was feared extinct until two specimens popped up on Ebay in 2018 one of which sold for over 9000.
The scientist intended on bringing the specimen home for closer analysis but the creature went down in a shipwreck off the Cape of Good Hope less than a year later. Ptychochromis only is a fish species that was become extinct by the IUCN International Union for Conservation of Nature however Onilahy River system is large so there might be a possibility of remaining populations in the remote areas of the river. Varanus douarrha was first encountered in 1823 by French naturalist René Lesson.