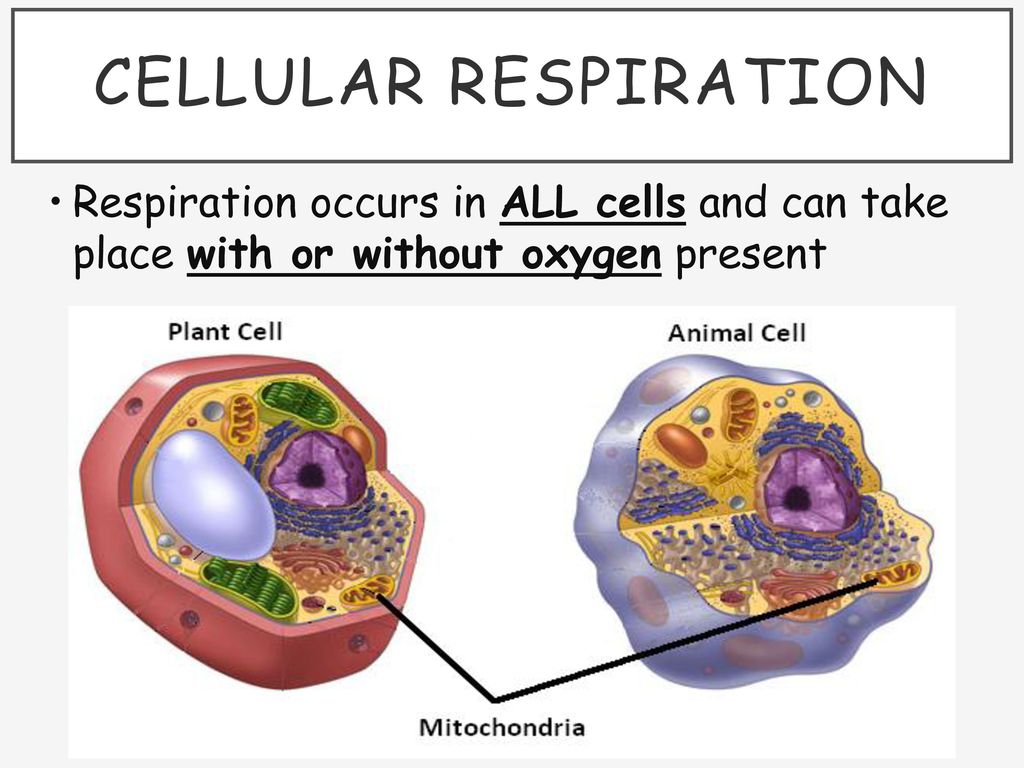
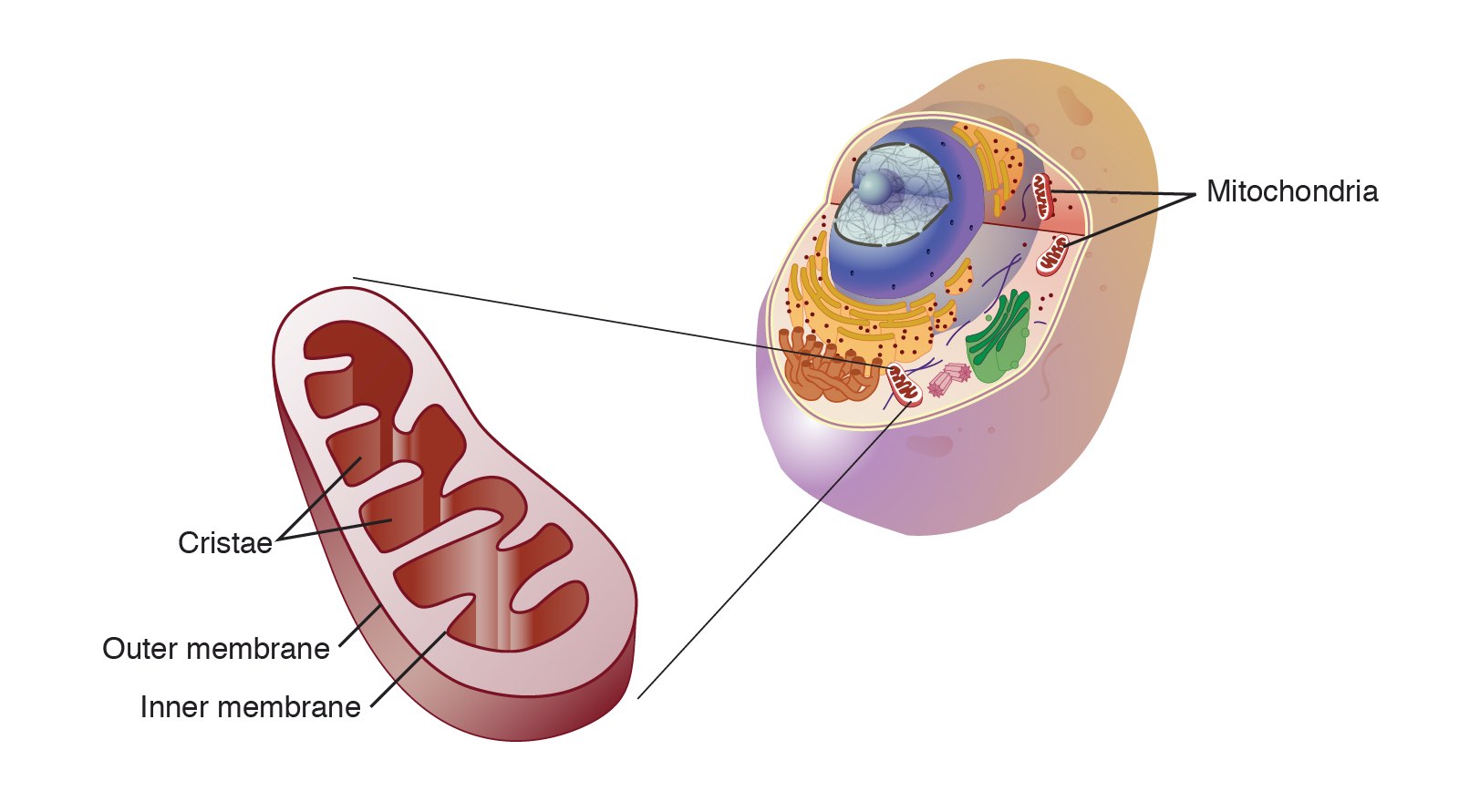
Cellular Respiration Takes Place In The Cells Of All Organisms

Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms.
Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms. While the process can seem complex this page takes you through the key elements of each part of cellular respiration. Heterotrophs like humans ingest other living things to obtain glucose. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration.
The overall process of cellular respiration takes place in a number of steps that are specialized for the degradation of specific molecules. Organisms from all kingdoms of life including bacteria archaea plants protists animals and fungi can use cellular respiration. Aerobic Respiration in Animals Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast Anaerobes.
Anaerobic respiration the first step in cellular respiration in all living cells is glycolysis which can take place without the presence of molecular oxygenif oxygen is present in the cell then the cell can subsequently take advantage of aerobic respiration via the tca cycle to produce much more usable energy in the form of atp than any anaerobic pathway. Cellular respiration begins in the cytoplasm of cells. The process of breakdown of glucose with the use of oxygen is called aerobic respiration.
Respiration In Organisms Class 7 Science Extra Questions and Answers Very Short Extra Questions and Answers. It occurs in autotrophs such as plants as well as heterotrophs such as animals. It is completed in mitochondria.
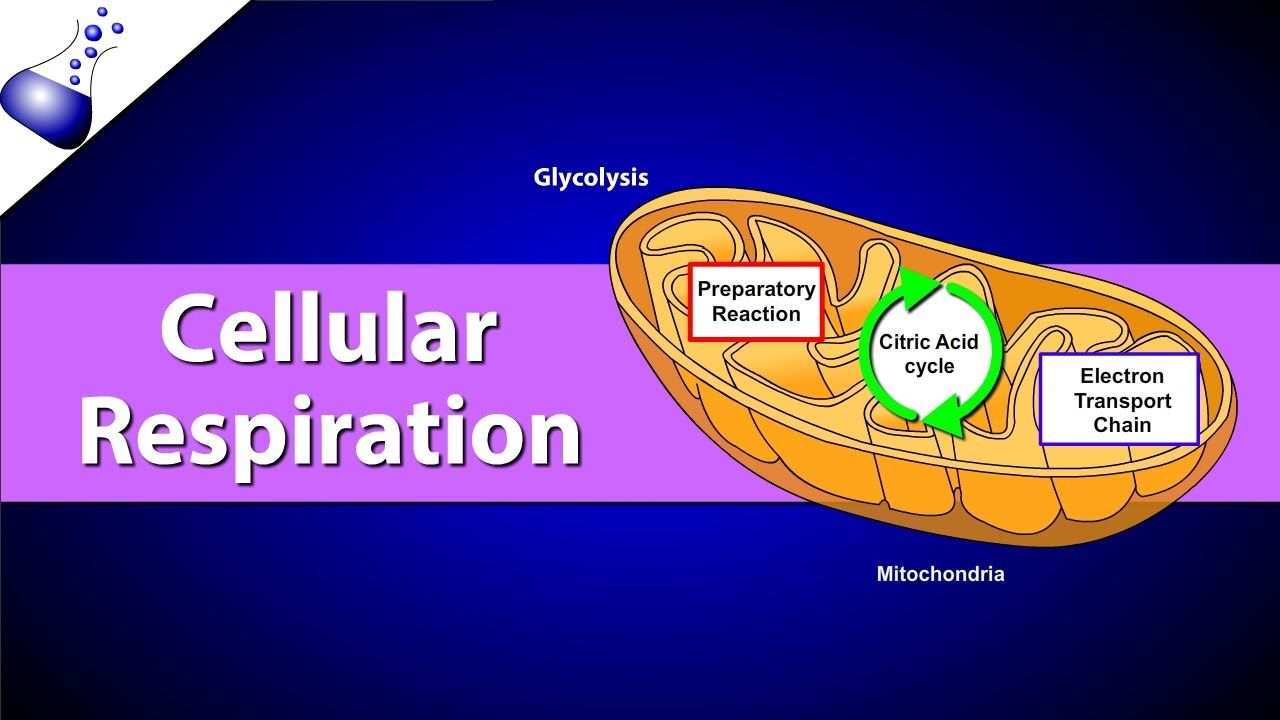
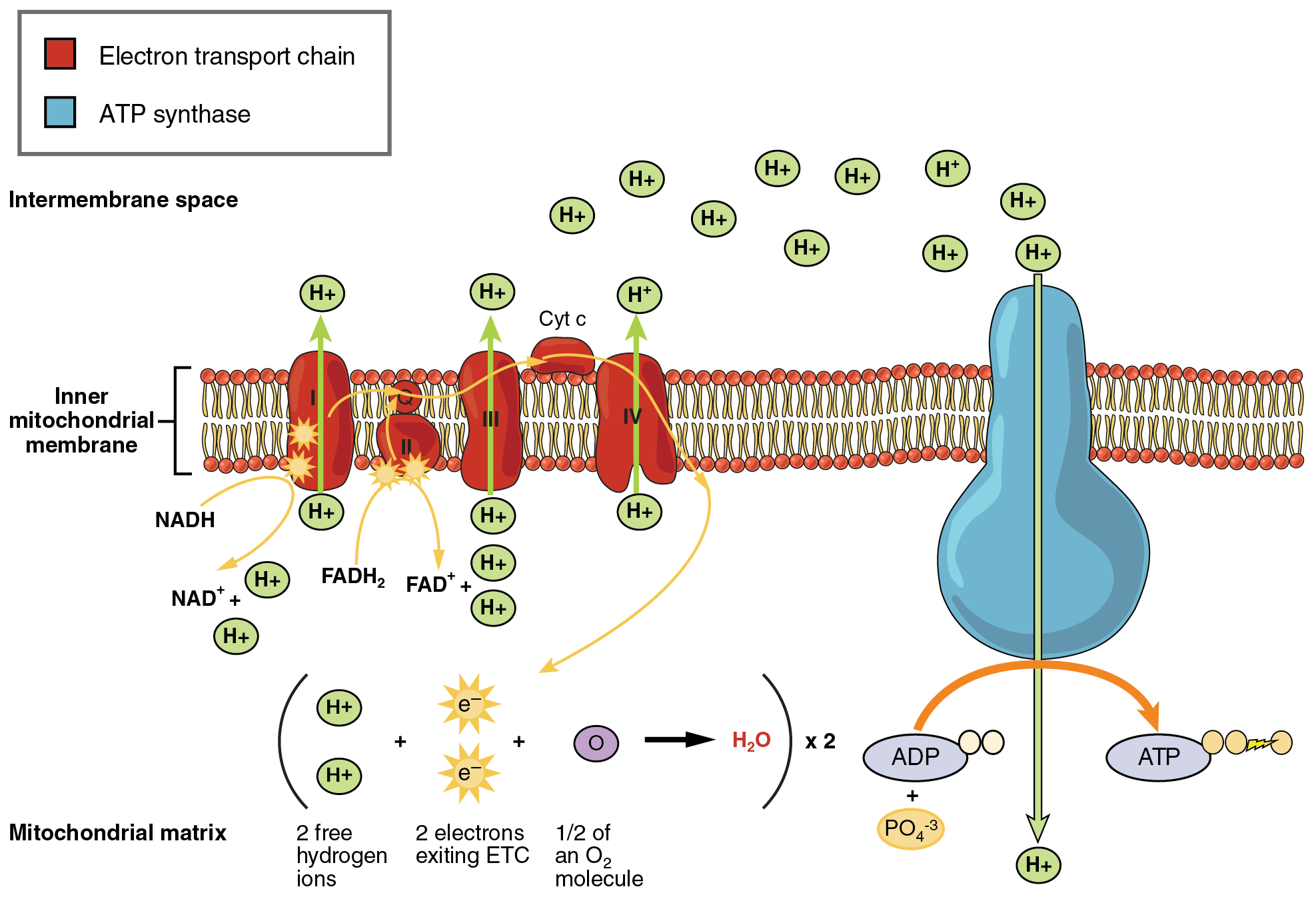
The reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages. Cellular respiration is essential in creating biochemical energy by converting different kinds of nutrients into adenosine triphosphate or ATP. Cellular respiration is the process in which cells break down glucose release the stored energy and use the energy to make ATP.
Glycolysis the Krebs cycle also called the citric acid cycle and electron transport. Where does cellular respiration occur group of answer choices. Each ATP molecules for.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)

/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)