Cellular Respiration Meaning In English
/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)
Cellular respiration in American English.
Cellular respiration meaning in english. Learn more in the Cambridge English-Chinese traditional Dictionary. Changes that allow gas exchange within cells 3. Cell respiration a catabolic process see catabolism occurring in cells where complex organic molecules are broken down to release energy for other cellular processes.
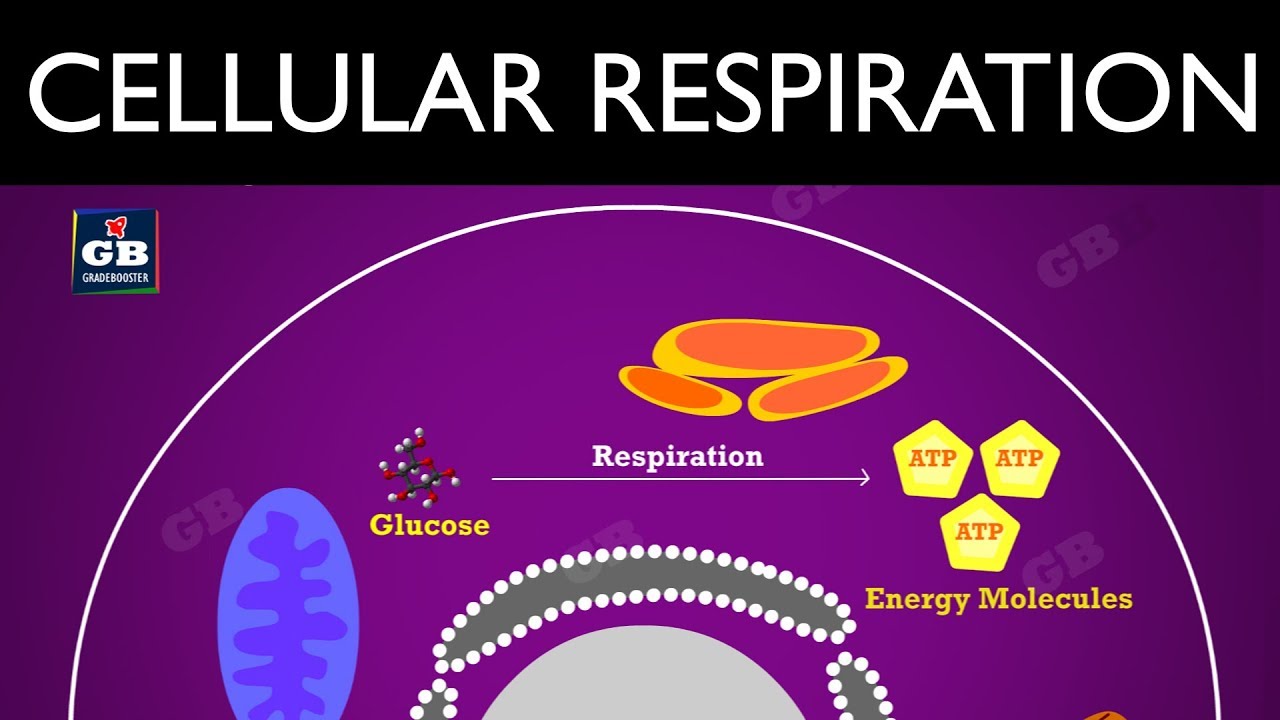
Respiration is the process by which stored organic materials carbohydrates proteins fats are broken down into simple end products with a release of energy. Processes that take place in the cells and tissues during which energy is released and carbon dioxide is produced and absorbed by the blood to. Why is cellular respiration important.
The metabolic processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules. Cell respiration usually occurs in the presence of oxygen see AEROBIC RESPIRATION but some organisms can respire without oxygen see ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION. Cellular respiration definition is - any of various energy-yielding oxidative reactions in living matter that typically involve transfer of oxygen and production of carbon dioxide and water as end products.
To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form. Most material 2005 1997 1991 by Penguin Random House LLC. 200 Phrases for saying THANK YOU in any situation.
Cell respiration usually occurs in the presence of oxygen see aerobic respiration but some organisms can respire without oxygen see anaerobic respiration. Processes that take place in the cells and tissues during which energy is released and carbon dioxide is produced and absorbed by the blood to be. Virag Cseke - November 21 2017.
Noun the metabolic processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules. The noun CELLULAR RESPIRATION has 1 sense. Cellular respiration- the metabolic processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/breathing_diagram-5c37af15c9e77c00013abdbd.jpg)





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aerobic_cellular_respiration-5c37aa17c9e77c0001c3f665.jpg)