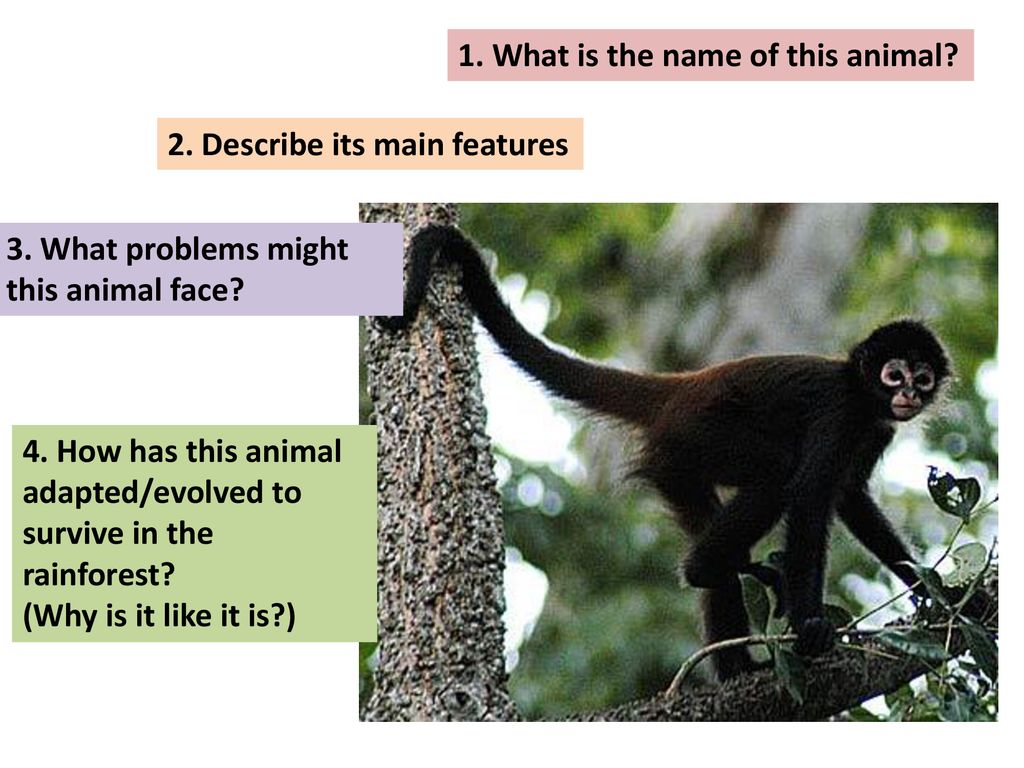
Amazon Rainforest Animals Adaptations

Grassland animals have adapted to dry and windy climate conditions.
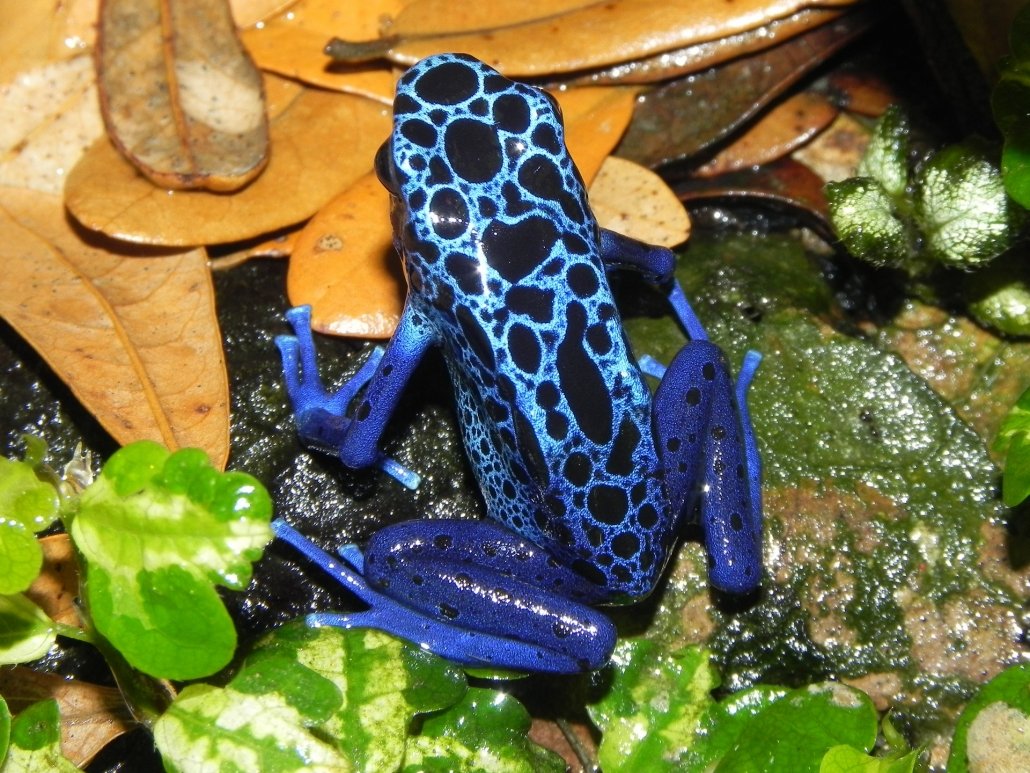
Amazon rainforest animals adaptations. In fact more than 20 of the worlds oxygen is produced in the Amazon Rainforest in South America due to the high number of plants living there. Many animals in the tropical rainforests of the world have adapted to either a nighttime or a daytime mode of life in order to survive. Animals like the flying fox bat and Wallaces flying frog face less competition from animals such as birds and diurnal reptiles when they hunt at night.
One example is the nocturnal Amazon tree boa a strikingly. Sloths have adapted to the rainforest ecosystem in several ways. The following adaptations allow plants to survive in the conditions of the rainforest.
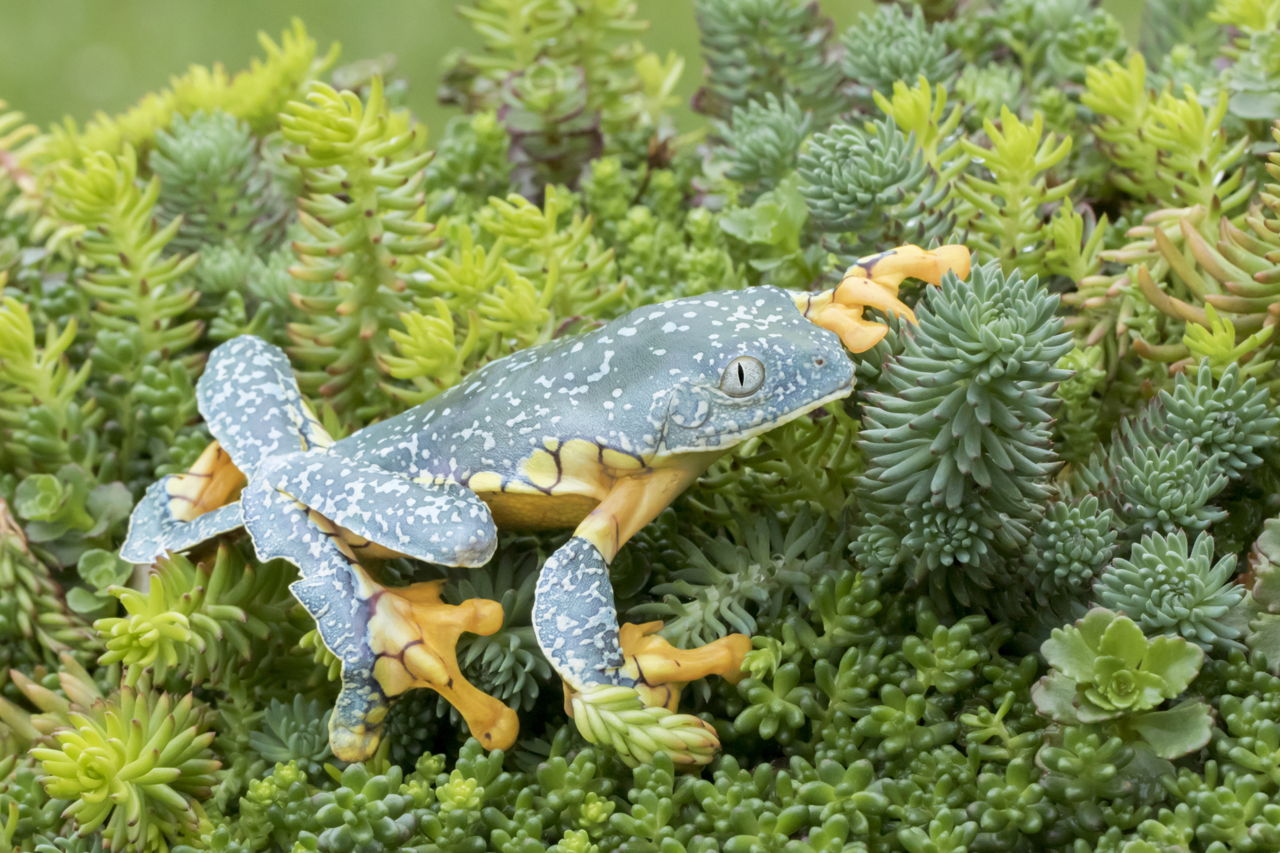
This lesson discovers how animals have adapted to the Amazon rainforest. Including examples of eight animals that have adapted to life in rainforest conditionsWith this pack pupils are asked to gather information from the examples provided and use their knowledge to design their own animal perfectly suited to rainforest lifeHelp your children learn all about animals that live in the rainforest with this teacher-made PowerPoint packFor more on the rainforest topic why not check out this brilliant Plants of the Rainforest. Animal adaptations many animals have adapted to the unique conditions of the tropical rainforests.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user. It covers areas including. Creative Commons Sharealike Reviews.
Glass Frogs family Centrolenidae Unusual animals. Black Caimans lay between 15 and 40 eggs but few will make it to adulthood due primarily to other animals stealing their eggs. How has the sloth adapted to the rainforest.
Tropical Rainforest Overview From the Amazon rainforest in South America to the lush rainforests of Australia and southeast Asia to the. Something went wrong please try again later. Many species of insects are also nocturnal so this gives insectivorous predators an opportunity to hunt.