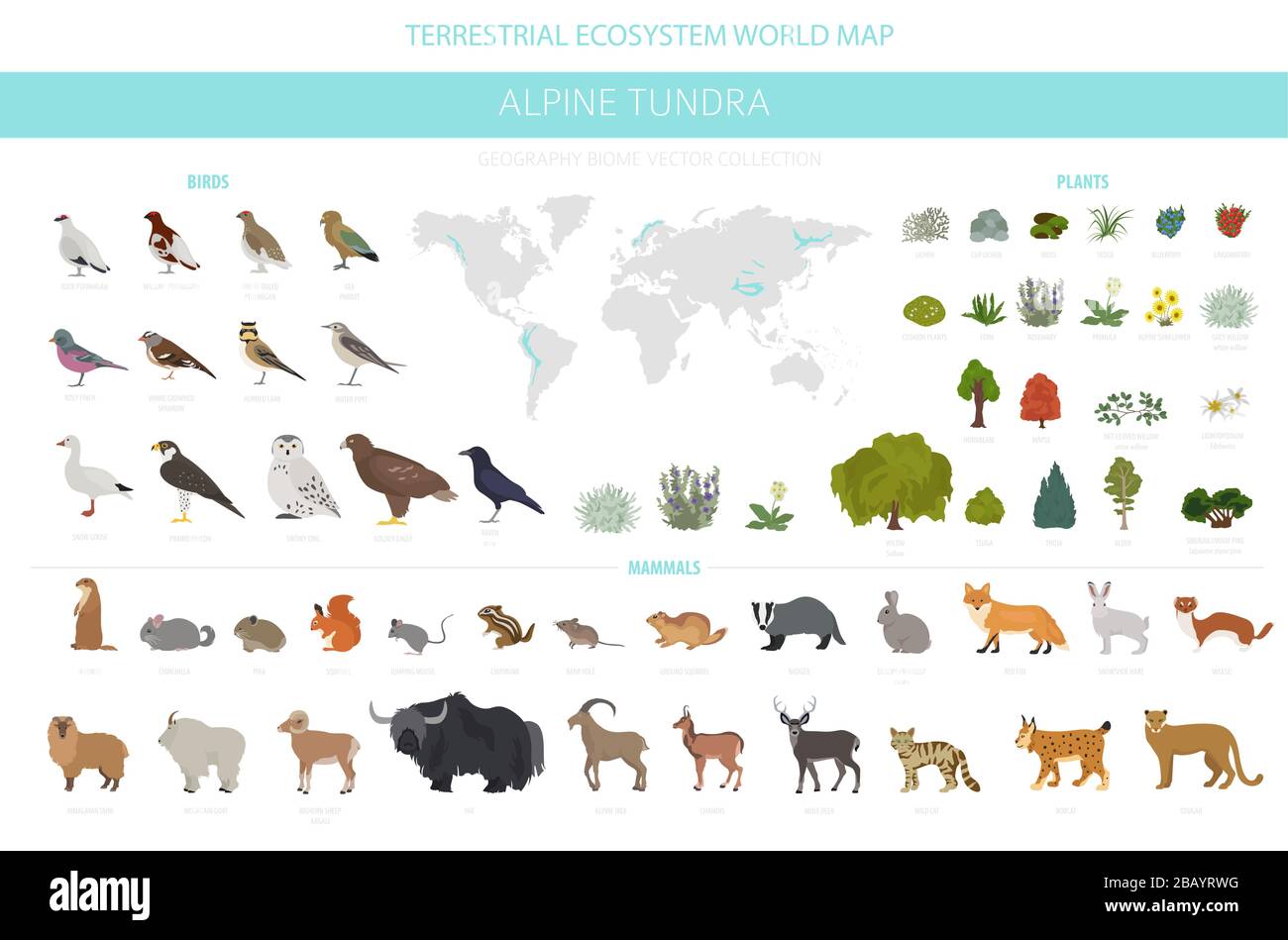
Alpine Tundra Animals Adaptations

Arctic tundra plants can photosynthesize at low temperatures at low light intensities and for long periods of daylight.
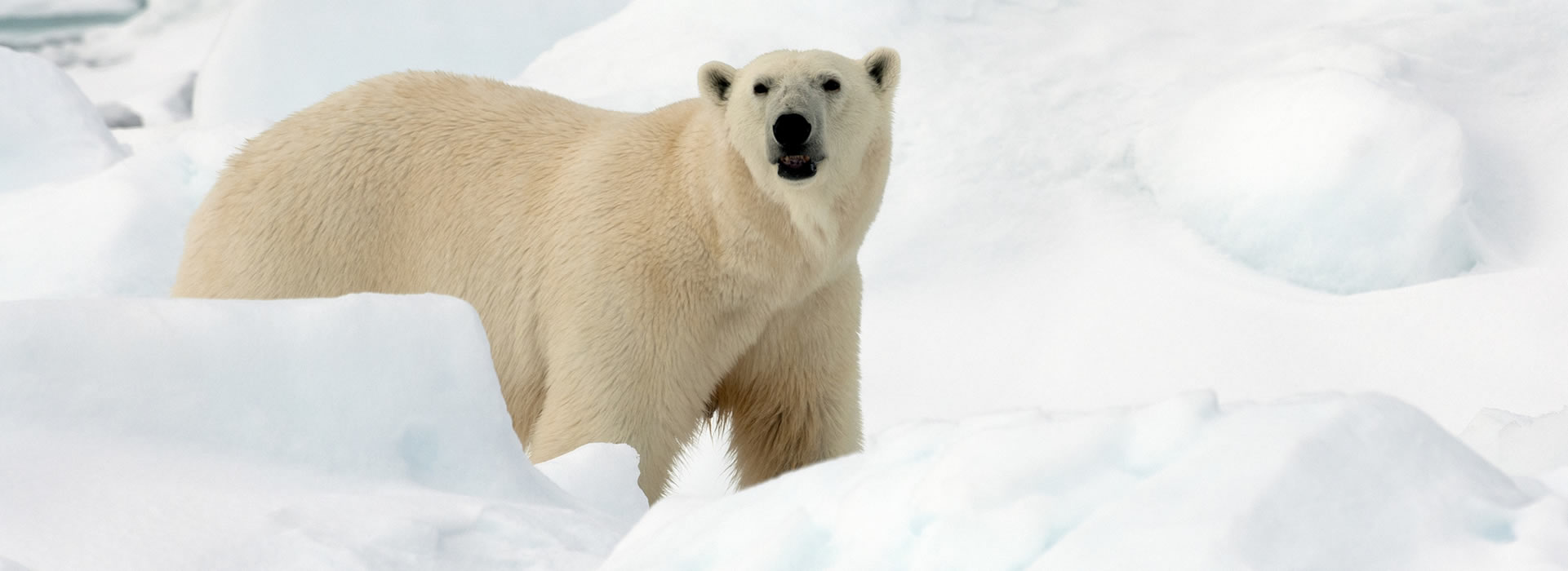
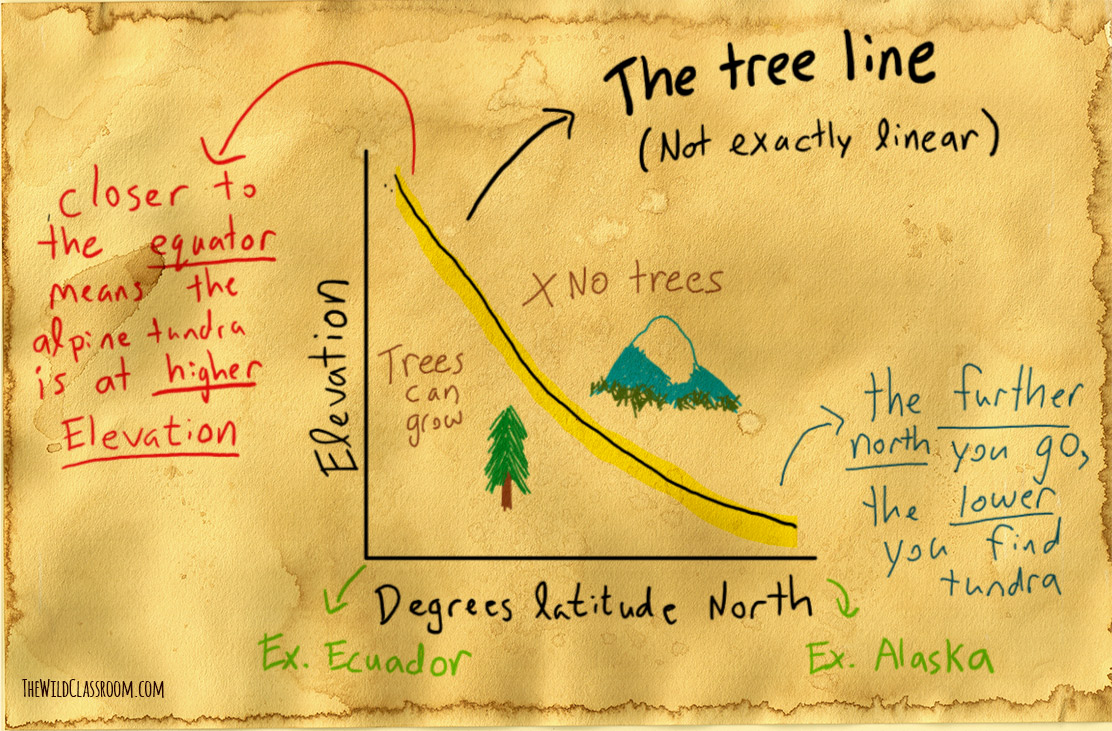
Alpine tundra animals adaptations. Their elevation normally ranges between 10000 feet 3000 meters and the area where a mountains snow line begins. The polar bear is one of most well known animals in the Alpine Tundra. Alpine biome describes an ecosystem that doesnt contain trees due to its high altitude.
Animals need shelter and insulation in the tundra. Animal adaptations in the tundra biome animals have many adaptations to survive in this harsh environment. Brief summers long winters brutal winds little precipitation and bone-chilling temperatures limit the plants and animals that can survive in the tundra but those that do are ingeniously adapted to the harsh conditions.
There are three types of tundra. The alpine biome provides a diversity of animals adapted to survive in the colder often snowy weather. Food and feeder relationships are simple and they are more subject to upset if a critical species disappears or decreases in number.
That are one to two years old. Life is difficult in the tundra the coldest type of climate on Earth. Animals in the alpine tundra migrate to lower elevations in winter to escape the cold and find food.
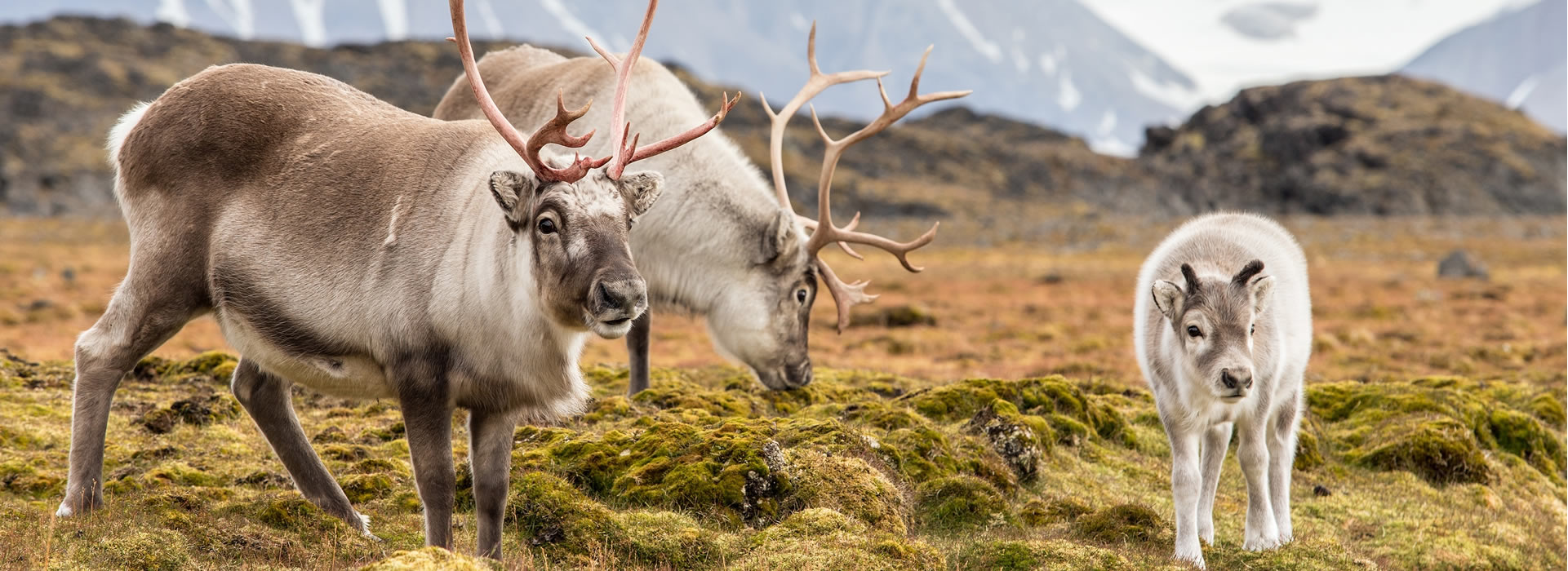
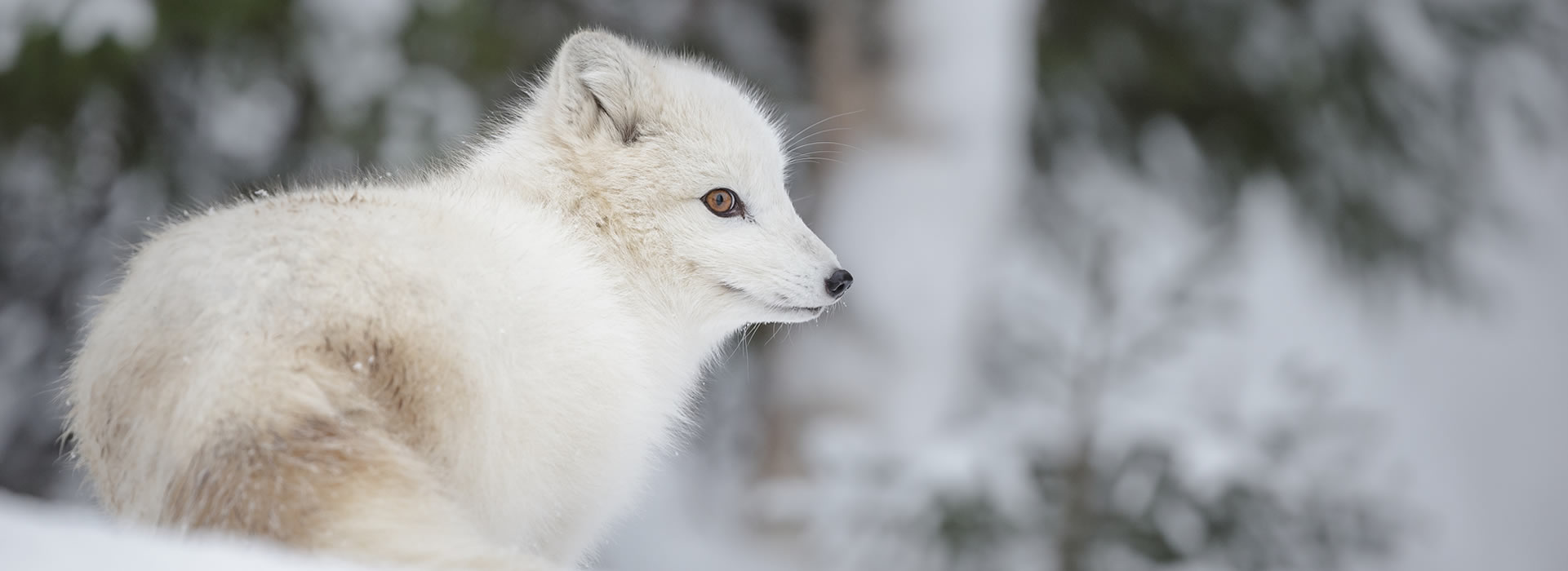
Tundra wildlife includes small mammalssuch as Norway lemmings Lemmus lemmus arctic hares Lepis arcticus and arctic ground squirrels Spermophilus parryii and large mammals such as caribou Rangifer tarandus. Adaptations for survival amidst drying winds and cold temperatures may make tundra vegetation seem very hardy but in some respects it remains very fragile. Lemmings arctic hares and arctic ground squirrels are a few animals that have adapted to the cold.
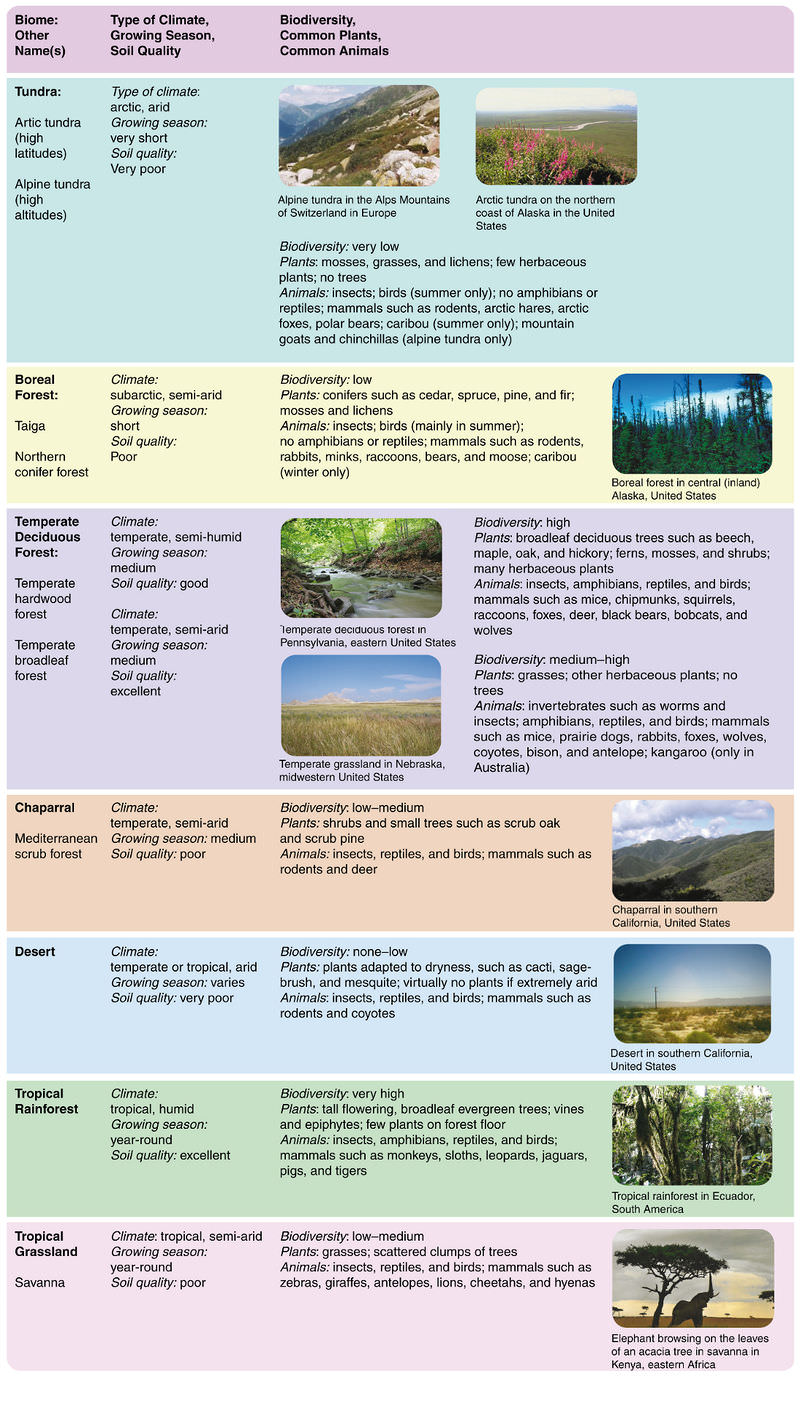
Climate Location Plants and Animals. These biomes are found in mountainous regions across the globe. The tundra is a treeless biome in which low temperatures and short growing seasons limit plant growth above a certain height.